How to Cure Gum Disease Without a Dentist: A Comprehensive Guide
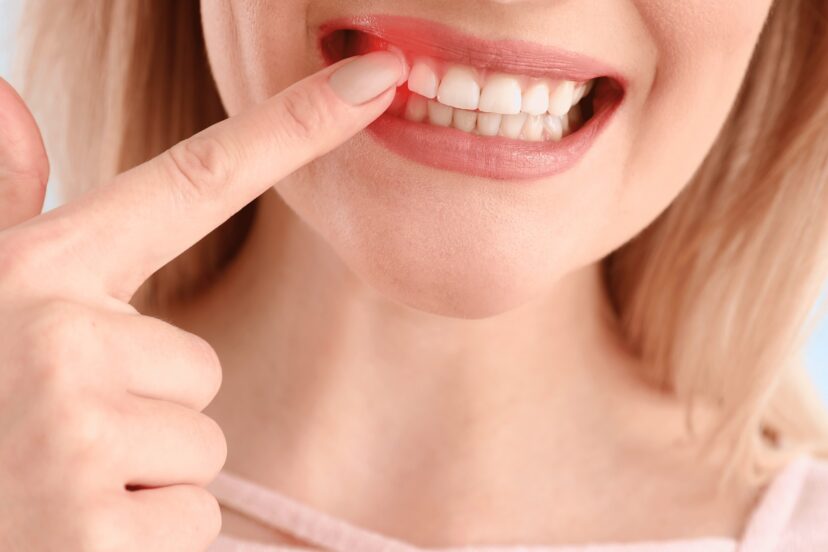
Are you experiencing swollen, bleeding gums or persistent bad breath?
It could be a sign of gum disease, a common oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide.
While professional dental care is essential for treating gum disease, there are steps you can take at home to alleviate symptoms and promote gum health.
In this guide, we’ll explore effective strategies on how to cure gum disease without a dentist, empowering you to take control of your oral health and restore your smile.
Understanding Gum Disease: The Silent Threat to Oral Health
Before we dive into how to cure gum disease without a dentist, let’s discuss what gum disease is and why it’s crucial to address it promptly.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth, including the gums and bone.
If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and may even contribute to systemic health issues such as heart disease and diabetes.
Recognizing the signs of gum disease and taking proactive steps to address them is key to preventing further damage and restoring gum health.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease: Know What to Look For
Identifying the early signs of gum disease is essential for prompt intervention and treatment.
Common symptoms of gum disease include:
- Swollen, tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pain or discomfort when chewing
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s essential to take action to address gum disease before it progresses further.
How to Cure Gum Disease Without a Dentist: Ten Home Remedies for Oral Health
While professional dental care is the gold standard for treating gum disease, there are several home remedies and self-care practices that can help alleviate symptoms and promote gum health.
Here are some effective strategies on how to cure gum disease without a dentist:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
The foundation of gum health is proper oral hygiene. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Don’t forget to floss daily to remove plaque and debris from between your teeth and along the gumline. - Use Antiseptic Mouthwash
Rinse with an antiseptic mouthwash containing ingredients like chlorhexidine or essential oils to reduce plaque and bacteria in the mouth. Swish the mouthwash around for 30 seconds to one minute before spitting it out. - Saltwater Rinse
A saltwater rinse can help soothe inflamed gums and reduce bacteria in the mouth. Mix a teaspoon of salt into a glass of warm water and swish it around your mouth for 30 seconds to one minute before spitting it out. - Oil Pulling
Oil pulling is an ancient practice that involves swishing oil around in your mouth to remove toxins and bacteria. Try swishing coconut oil or sesame oil in your mouth for 10-15 minutes before spitting it out and rinsing with water. - Turmeric Paste
Turmeric has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties that can help reduce gum inflammation and fight bacteria. Mix turmeric powder with water to form a paste, then apply it to your gums and leave it on for a few minutes before rinsing. - Aloe Vera Gel
Aloe vera gel has soothing properties that can help reduce gum inflammation and promote healing. Apply a small amount of pure aloe vera gel to your gums and massage gently for a few minutes before rinsing. - Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is known for its antimicrobial properties and can be used to combat gum disease. Dilute a few drops of tea tree oil in water and use it as a mouthwash, being careful not to swallow it. - Dietary Changes
A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support gum health and overall well-being. Avoid sugary and processed foods, which can contribute to gum inflammation and bacterial growth. - Quit Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease and can hinder the healing process. If you smoke, consider quitting to improve your oral health and reduce your risk of gum disease. - Stress Reduction
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and exacerbate gum disease. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to support overall health and well-being.
ProvaDent: The Natural Secret to Oral Health
If you’re seeking a natural and effective solution for gum disease and overall oral health, ProvaDent offers a scientifically formulated supplement designed to support your dental wellness. Developed by Dr. Knudson, a board-certified dentist with extensive experience in oral biology, ProvaDent combines potent natural ingredients to address common dental issues such as gum inflammation, plaque buildup, and bad breath.
Key Benefits of ProvaDent:
- Balances Oral Microbiome: ProvaDent contains four strains of probiotics that help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the mouth, reducing harmful pathogens that contribute to gum disease and tooth decay.
- Reduces Gum Inflammation: Ingredients like cranberry extract and purple carrot powder are rich in antioxidants, which help soothe inflamed gums and support overall gum health.
- Prevents Plaque Formation: The BioFresh™ Clean Complex targets dental biofilm, effectively breaking down plaque without disrupting beneficial oral bacteria.
- Freshens Breath Naturally: Organic xylitol not only sweetens but also inhibits the growth of odor-causing bacteria, promoting fresher breath.
Customer Testimonials:


Special Offer:
ProvaDent is currently available at a discounted rate:
- 6 Bottles (180-Day Supply): $49 per bottle (Free Shipping)
- 3 Bottles (90-Day Supply): $59 per bottle (Free Shipping)
- 1 Bottle (30-Day Supply): $69 per bottle (+$9.99 Shipping)
Each purchase is backed by a 60-day money-back guarantee, ensuring your satisfaction.
To learn more or to place an order, visit ProvaDent Official Site
When to Seek Professional Help: Knowing When It’s Time to See a Dentist
While home remedies can be effective for alleviating symptoms of gum disease, they are not a substitute for professional dental care.
If you have persistent or severe symptoms of gum disease, it’s essential to seek prompt treatment from a dentist.
A dentist can perform a thorough evaluation of your oral health, provide professional cleanings and treatments, and offer personalized recommendations for managing gum disease.
Summary: Taking Charge of Your Oral Health
In conclusion, gum disease is a common but treatable condition that requires proactive management to prevent complications and restore gum health.
By practicing good oral hygiene, incorporating home remedies into your routine, and seeking professional dental care when needed, you can effectively address gum disease and maintain a healthy smile for years to come.
FAQs about How to Cure Gum Disease Without a Dentist:
- Can gum disease be cured without professional dental care?
While home remedies can help alleviate symptoms of gum disease, they are not a substitute for professional dental care. It’s essential to see a dentist for a thorough evaluation and treatment if you have gum disease. - How long does it take to cure gum disease at home?
The timeline for curing gum disease at home varies depending on the severity of the condition and how consistently you follow home remedies. Some people may experience improvement within a few weeks, while others may require longer-term management. - Are home remedies safe for treating gum disease?
When used correctly, many home remedies for gum disease are safe and effective. However, it’s essential to follow instructions carefully and consult with a dentist if you have any concerns or underlying health conditions. - What are the risks of untreated gum disease?
Untreated gum disease can lead to serious complications, including tooth loss, bone damage, and systemic health issues such as heart disease and diabetes. It’s crucial to address gum disease promptly to prevent further damage. - How can I prevent gum disease from recurring?
To prevent gum disease from recurring, practice good oral hygiene, maintain a healthy diet, avoid smoking, and attend regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Consistent preventive care is key to long-term gum health.
References:
- “Effectiveness of Saltwater Rinse for Periodontal Health” by Chaves et al. (2014):
This study investigated the effectiveness of saltwater rinses in promoting periodontal health. The findings suggested that saltwater rinses can help reduce inflammation and bacterial load in the mouth, contributing to improved gum health and reduced symptoms of gum disease. - “Antimicrobial Properties of Tea Tree Oil in Periodontal Care” by Soukoulis et al. (2015):
Researchers examined the antimicrobial properties of tea tree oil and its potential use in periodontal care. The study found that tea tree oil exhibits antimicrobial activity against oral pathogens, making it a promising natural remedy for managing gum disease. - “Effect of Aloe Vera Gel on Gingival Inflammation” by Gupta et al. (2013):
This study evaluated the effects of aloe vera gel on gingival inflammation in patients with gum disease. Results showed that aloe vera gel applied topically to the gums helped reduce inflammation and improve gum health, indicating its potential as an adjunct treatment for gum disease. - “Turmeric and Curcumin in Periodontal Therapy” by Kaur et al. (2016):
Researchers reviewed the literature on the use of turmeric and its active compound, curcumin, in periodontal therapy. The review highlighted the anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties of curcumin, suggesting its potential as a natural treatment for gum disease. - “Effectiveness of Oil Pulling in Oral Health Maintenance” by Peedikayil et al. (2015):
This study investigated the effectiveness of oil pulling, a traditional oral hygiene practice, in maintaining oral health. The findings indicated that oil pulling with coconut oil can help reduce plaque buildup, improve gum health, and alleviate symptoms of gum disease. - “Role of Probiotics in Oral Health: A Systematic Review” by Twetman et al. (2015):
Researchers conducted a systematic review to evaluate the role of probiotics in promoting oral health, including gum disease prevention and treatment. The review suggested that certain probiotic strains may help reduce gingival inflammation and improve gum health when used as adjuncts to conventional periodontal therapy. - “Efficacy of Vitamin C Supplementation in Periodontal Therapy” by Chapple et al. (2017):
This study examined the efficacy of vitamin C supplementation in supporting periodontal therapy outcomes. Results indicated that vitamin C supplementation may have beneficial effects on gum health, including reduced gingival inflammation and improved wound healing following periodontal treatment. - “Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Periodontal Health” by Iwasaki et al. (2015):
Researchers investigated the effects of omega-3 fatty acids on periodontal health and inflammation. The study found that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation may help reduce gingival inflammation and improve gum health in patients with gum disease. - “Impact of Stress Reduction Techniques on Periodontal Health” by Tomar et al. (2018):
This study explored the impact of stress reduction techniques, such as meditation and yoga, on periodontal health. Results suggested that stress reduction techniques may help reduce gingival inflammation and improve gum health by modulating the body’s inflammatory response. - “Effectiveness of Herbal Mouthwashes in Periodontal Care” by Shakya et al. (2016):
Researchers evaluated the effectiveness of herbal mouthwashes containing ingredients like neem, clove, and peppermint in periodontal care. The study found that herbal mouthwashes demonstrated antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, making them promising adjuncts to conventional periodontal therapy for managing gum disease.